Gallbladder cancer is a rare but aggressive malignancy that begins in the gallbladder, a small, pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver. The gallbladder’s primary function is to store bile, a digestive fluid that helps break down fats. Unfortunately, gallbladder cancer often goes undetected in its early stages because it typically does not cause noticeable symptoms. By the time it is diagnosed, it has often spread to other parts of the body, making treatment more challenging.
In Nepal, gallbladder cancer is becoming a growing concern, and early detection can significantly improve survival rates. Dr. Sudip Shrestha, a leading oncologist in Nepal, emphasizes the importance of awareness, early diagnosis, and proper medical intervention to combat this disease effectively.
What is Gallbladder Cancer?
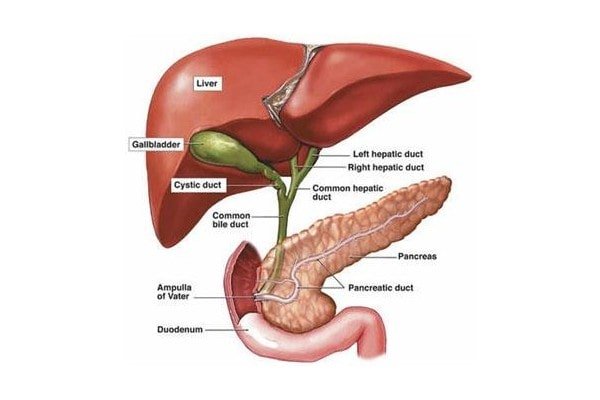
Gallbladder cancer occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the gallbladder, forming a tumor. The most common type of gallbladder cancer is adenocarcinoma, which begins in the glandular cells that line the gallbladder’s inner surface.
Why is Gallbladder Cancer Dangerous?
- Late Diagnosis: Symptoms are often vague and resemble other digestive disorders, delaying diagnosis.
- Fast Spread: The gallbladder is close to the liver, bile ducts, and other organs, making it easier for cancer to spread.
- Limited Awareness: In Nepal, many people are unaware of gallbladder cancer, leading to late-stage detection and poor survival rates.
Symptoms of Gallbladder Cancer
In the early stages, gallbladder cancer may not cause noticeable symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, the following symptoms may appear:
- Abdominal Pain: Persistent pain, especially in the upper right side of the abdomen.
- Bloating: A feeling of fullness or swelling in the stomach.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes, which occurs when the bile ducts are blocked.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying.
- Lump in the Abdomen: A mass that can be felt in the upper right part of the belly.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Digestive discomfort and a loss of appetite.
When to See a Doctor?
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially persistent abdominal pain and jaundice, consult a doctor immediately. Early diagnosis can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes.
Causes and Risk Factors of Gallbladder Cancer
While the exact cause of gallbladder cancer is not always clear, several factors increase the risk of developing this disease:
1. Gallstones and Chronic Gallbladder Inflammation
Gallstones are the most common risk factor for gallbladder cancer. These hard deposits in the gallbladder can cause long-term irritation and inflammation, increasing the risk of cancerous changes.
2. Age and Gender
- Gallbladder cancer is more common in people over the age of 65.
- Women are more likely to develop gallbladder cancer than men, possibly due to hormonal influences.
3. Obesity and Diet
- Obesity increases the risk of gallbladder cancer as it is linked to gallstones and chronic inflammation.
- A diet high in unhealthy fats and low in fiber can contribute to gallbladder disease.
4. Family History
A family history of gallbladder cancer or other biliary tract cancers may increase the likelihood of developing the disease.
5. Exposure to Certain Chemicals
Workers in industries that involve metal or rubber manufacturing may be exposed to harmful chemicals that increase cancer risk.
Diagnosis of Gallbladder Cancer
Early detection of gallbladder cancer is crucial for successful treatment. Doctors may use the following tests to diagnose gallbladder cancer:
- Ultrasound: The first imaging test used to check for gallbladder abnormalities.
- CT Scan or MRI: Provides detailed images to determine if the cancer has spread.
- Biopsy: A sample of tissue is taken and examined under a microscope.
- Blood Tests: Liver function tests and tumor markers can indicate gallbladder abnormalities.
Treatment Options for Gallbladder Cancer
The treatment for gallbladder cancer depends on the stage of the disease. Common treatments include:
1. Surgery
- If detected early, cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal surgery) may be performed to remove the cancer.
- In advanced cases, surgery may involve removing surrounding tissues and lymph nodes.
2. Chemotherapy
- Used to kill cancer cells, either before or after surgery.
- In late-stage cases, chemotherapy can help slow the disease and relieve symptoms.
3. Radiation Therapy
- High-energy rays target and destroy cancer cells, often used in combination with other treatments.
4. Palliative Care
- For advanced cases, treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and improving quality of life.
Can Gallbladder Cancer Be Prevented?
While there is no sure way to prevent gallbladder cancer, certain lifestyle changes can reduce the risk:
✅ Maintain a Healthy Weight – Obesity is a major risk factor. Exercise regularly and eat a balanced diet.
✅ Eat a Healthy Diet – Increase fiber intake and avoid processed and fatty foods.
✅ Quit Smoking – Smoking increases the risk of many cancers, including gallbladder cancer.
✅ Monitor Gallstones – If you have gallstones, consult a doctor to determine if treatment is needed.
✅ Regular Health Check-ups – Early detection is key to successful treatment.
Gallbladder Cancer in Nepal: Expert Insights from Dr. Sudip Shrestha
Dr. Sudip Shrestha, one of Nepal’s leading oncologists and the founder of Nepal Cancer Hospital and Research Center, has been at the forefront of cancer treatment and awareness. He emphasizes that early detection and prevention are the most effective strategies against gallbladder cancer.
According to Dr. Shrestha:
📌 Awareness is crucial – Most people in Nepal do not recognize the symptoms of gallbladder cancer until it is too late. Public education can help in early diagnosis.
📌 Regular screenings for at-risk individuals – People with gallstones, chronic gallbladder inflammation, or a family history of gallbladder disease should undergo regular medical check-ups.
📌 Access to advanced cancer care – Nepal has made progress in cancer treatment, but more awareness and resources are needed to improve early diagnosis rates.
Conclusion
Gallbladder cancer is a serious but preventable disease. While it is not common, its late diagnosis often leads to poor outcomes. By recognizing the symptoms early, understanding risk factors, and consulting experts like Dr. Sudip Shrestha, individuals in Nepal can improve their chances of successful treatment.
If you or someone you know is experiencing persistent abdominal pain, jaundice, or other symptoms related to gallbladder cancer, do not delay seeking medical attention. Early intervention can save lives.



